Chiari Malformation Type III with Good Outcome: Case-Report and Review of Clinical and Radiological Findings-Juniper publishers
JUNIPER PUBLISHERS-OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL OF HEAD NECK & SPINE SURGERY
Abstract
Chiari III malformation, one of the rare variants of
Chiari malformations, is including a small dysplastic posterior fossa,
hydrocephalus, medullary abnormalities, and hindbrain herniation into a
low occipital/high cervical encephalocele. This type can be lethal if
not treated and is related to severe neurological deficits, so surgical
care should immediately be undertaken. We are presenting a 1.5-month-old
male infant with Chiari III malformation that was managed surgically
with good outcome in addition, review the radiological, clinical and
pathogenesis of Chiari III malformation.
Type III Chiari malformation is a very rare condition
that is described by Chiari in 1891.This type of Chiari defined as
hindbrain herniation into a high cervical encephalocele or low
occipital, and osseous defects with features of type II Chiari
malformation (including a small posterior fossa, herniated dysplastic
posterior fossa content, hydrocephalus, medullary kinking, and tectal
beaking) [1-5]. In literature, approximately 60 cases have been reported since 1891 to have Chiari III (Table 1).
Chiari III malformation is related to early
mortality, if not being treated. Since it has a poor outcome, it is
related to severe neurological deficits, developmental delays, and
seizure in long term, if being survived [6].
We are presenting a 1.5-month-old case of Chiari type III that was
managed surgically with good outcome. In addition, review the
pathogenesis, radiological, and clinical features of Chiari III
malformation.
Case
A 1.5-month-old male infant presented to hospital
emergency department with complaint of large congenital occipital mass.
He was born at full-term, as the product of normal delivery, second
child of a low socioeconomic non-consanguineous parents. There was no
history of medication or maternal infection. The mother had no history
of use of iron products, too. On examination, the child had 3350gr
weight (wt.), 32 cm head circumference (H.C.) at birth, and 4000gr wt.,
36cm H.C. at the day of admission. He had no neurological deformity or
cranial nerve palsy, and had normal eye movement with no nystagmus.
Spontaneous movements of all extremities were present. All reflexes were
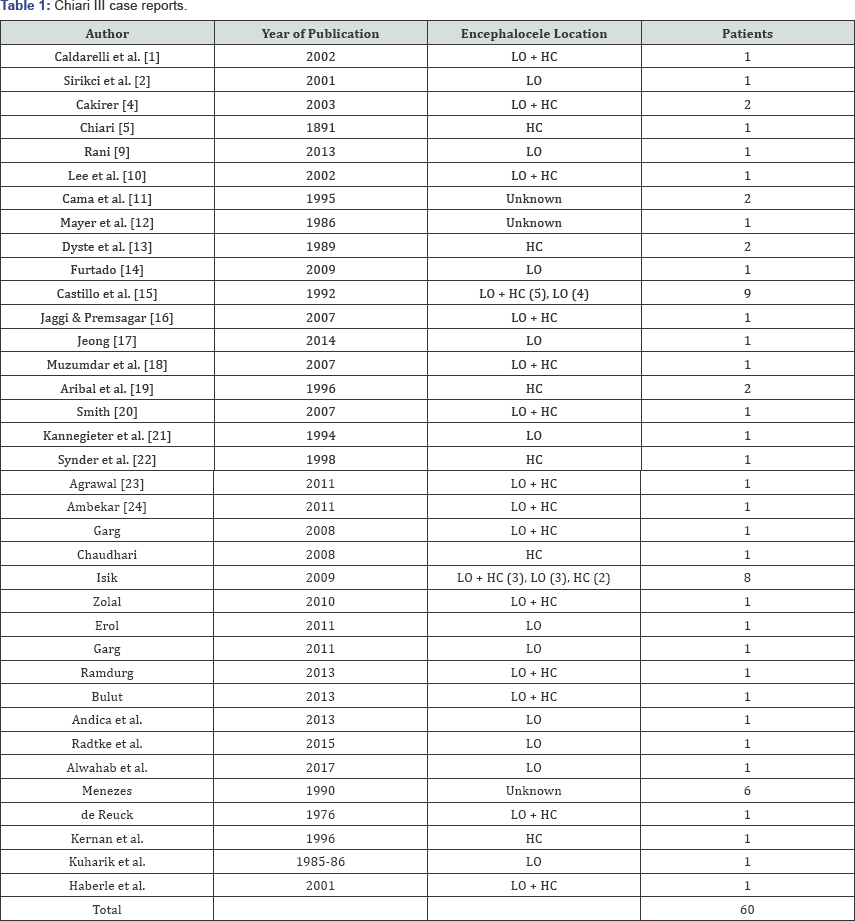
normal. Chest was clear, with normal breathing sound. There was a soft,
6*5cm trans-illuminate mass in occipital and upper cervical region,
which was tense on crying and was covered with thin skin (Figure 1).
There was no cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage. There was no history of
fever or discharge from the mass. The biochemical and hematological
parameters were normal.
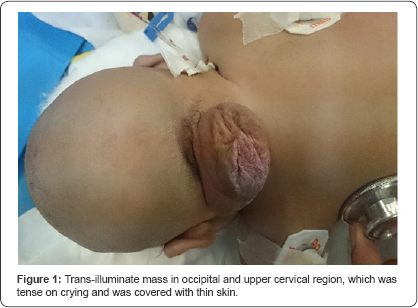
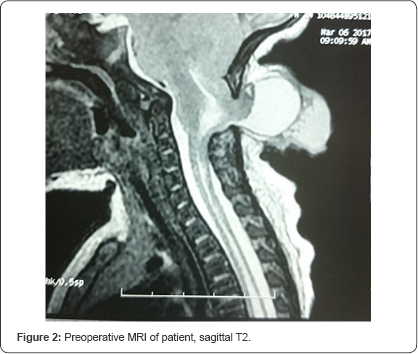
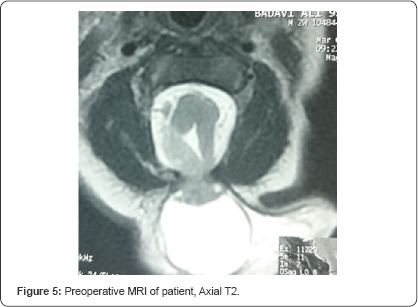
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) was performed on a
1.5T MR scanner and revealed a bony defect (approximately 2*2cm) in the
occipital and upper cervical (C1-C2 vertebrae) region that had an
encephalocele with partial herniation of the cerebellum and a part of
the brainstem. There was no hydrocephalus (Figure 2-5). No tethering or syringomyelia was revealed in screening MRI of the lumbar spine.

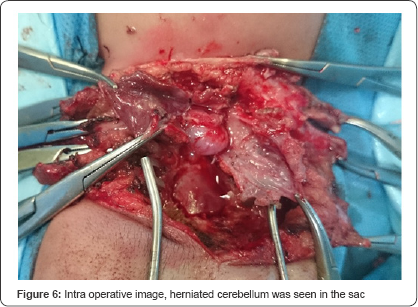
After general anesthesia, the patient was turned
prone. The skin over the mass was incised in midline and was dissected
around the mass. Below the skin, the covering dura was seen.
Suboccipital craniotomy was done. On opening the dura, herniated
cerebellum was seen in the sac (Figure 6).
Cord and brain steam was untethered and cranio-cervical junction
adhesions were released. There was no need for ventrico- peritoneal
shunt. Secondary closure of the dura was done with the pericranial
patch. The child was extubated in the recovery room. Early post
operation and on the fifth day brain computed tomography (CT) scan was
done that didn't show hydrocephalus. Examination of lower cranial nerve
was normal. Postoperative imaging revealed well positioned brain steam
and cerebellum (Figure 7).
Patient was discharged a week after surgery. Till now, 1 year after
surgery, patient has good outcome with normal developmental and
neurological examination.

Discussion
Hans Chiari, described and characterized hindbrain deformities as the Chiari malformation in 1891 [5].
One of the rare variants is Chiari malformation type III, that is
characterized by osseous defects and occipital or high cervical
encephalocele and some anatomical characteristics of Chiari malformation
type II, including a small posterior fossa, herniated dysplastic
posterior fossa content, hydrocephalus, medullary kinking, and tectal
beaking [1-4].
Chiari malformation type III has poorer outcomes that type I and II,
and those who survive develop with developmental delays and severe
neurological deficit [6].
Till now, the pathogenesis of Chiari malformation
type III remains unclear, but Chiari believed this variant was due to
hydrocephalus [5]. Some have suggested that primary abnormal mesodermal defect is related to this type [7].
Some authors have stated that during intrauterine period, escape of CSF
from an open neural tube defect has caused destination of primitive
ventricles and small skull, like what happens in Chiari II malformation [8].
Others believe that caudal displacement of hindbrain and hypoplastic
posterior fossa are the result of lack of distension of the embryonic
ventricular system secondary to abnormal neurulation [4].
Others have posited that failure of ossification centers to fuse
completely or failure of induction of endochondral bone by incomplete
closure of the neural tube are responsible for bony defects and
encephalocele [4,9].
Finally, some believe that mesenchymal development disturbance in
embryological life is the secondary event in Chiari III malformation and
the underlying problem is likely to be the deranged CSF dynamics [10].
Chiari III malformation incidence is 0.65-4.4% among all of the Chiari malformations [11-13] and have been diagnosed prenatally to 14-years-old [4]. The most common to the least position of encephalocele are low occipital/high cervical [14,15].
Symptoms are strongly related to the amount of herniated brain
structures, ranges from asymptomatic in those with only bulging in the
back of the head [16]
to clinical findings like downbeat nystagmus and titubation, ataxia,
sensory loss, respiratory failure, hyperreflexia, spastic muscle or
hypotonia, and inspiratory stridor [17,18].
Occipital bone defects are seen in some, but not all Chiari III malformations [19], and 70% of cases have been reported to have incomplete fusion of the posterior arches of C1 [4].
Contents of encephalocele in Chiari malformation III is usually
nonfunctional and contains necrosis of neural tissue, gliosis, fibrosis,
meningeal inflammation, cerebral or cerebellar tissue, ventricles, and
reactive astrocytes [6,15].
Cerebellum, occipital lobe, and parietal lobe are the most to the least
common parts of brain occurring in the sac. Ectopic venous sinuses and
aberrant deep veins are common [15].
Other anomalies of the brain are including posterior falx cerebri
aplasia, lack of cerebellum, posterior petrous pyramids and the clivus
scalloping, syringomyelia, and creeping of the cerebellar hemispheres
around the brain stem [4,15]. Though hydrocephalus is not an essential finding, has been reported in 88% of the cases [6]. Syringomyelia is commonly present [16,18].
Ultrasound has been used antenatally, the earliest report is at 18 weeks of gestational age (WGA) [20], to identify cranial anomalies [3,21]. Elective C section is the standard plan of delivery when encephalocele diagnosed [20]. MRI is the modality of choice and can identify the amount of brain occurring in the encephalocele [6,15], and is used prenatally after abnormalities were seen on fetal ultrasound [20].
Though occipital/cervical encephalocele is not necessarily associated
with a poor prognosis, Chiari III malformation can be lethal if
untreated, so surgical care should be undertaken.
Time of surgery remains controversial, some believe
that immediate closure of the defect is the ideal treatment while others
believe if the sac is covered with normal skin, it is rarely needed to
perform surgery urgently [6,16], but primary closure remains the treatment of choice [6,15].
Preserving neurological function while as much as possible neural
tissue in the encephalocele is resected, reconstruction and repair of
dura, and preventing future tethering are the goals of surgery [6,15]. Some authors report placing a temporary external drain [1], or a shunt before encephalocele closure [22-24]. Overall mortality rate is 29% [7,25], and postoperative mortality accounts for 22% of all mortalities [15]. Neurological function outcomes depend on the neurological status before surgery [24]. Positive prognostic factor is less than 5cm of herniated brainstem [6],
and hydrocephalus, neural tissues in the sac, large size of sac, and
intermittent respiratory stridor are the negative prognostic factors [7,18].
To know more about Open Access Journal of
Head Neck & Spine Surgery please click on:
To know more about Open access Journals
Publishers please click on : Juniper Publishers
Comments
Post a Comment