Mucosal Immunology of Human Head-Juniper publishers
JUNIPER PUBLISHERS-OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL OF HEAD NECK & SPINE SURGERY
Abstract
The theme for the immune system of human head is of
tripartite nature. The common mucosal immune compartment, the
mononuclear phagocyte cell system and the transudate cellular and
humoral factors of the systemic immunity. These compartments were
covering; natural, cross-road adaptive immune events outcomes. Among
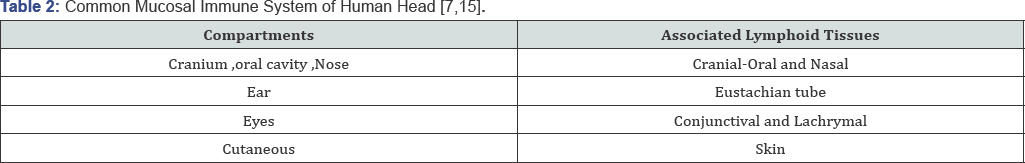
which, the common mucosal immune system, which can be mapped into;
Cranial- Oral and nasal associate lymphoid tissue, conjunctiva and
lachrymal associated lymphoid tissue ,Eustachian tube associate lymphoid
tissue, nasopharyngeal associated lymphoid tissue as well as facial
skin associated lymphoid tissue. In addition to the mononuclear
phagocyte cell system and the natural immune barriers.
Introduction
In my previous communication [1] that has been concerning otolaryn-giologic mucosal immune compartment and the second that was devoted to neck immunology [2]. The objective of the present micro- review was at the mucosal immunology of human head.
Biology

SAS: Skull associated structures
*These macrophages are mostly of migratory nature.

From an at a glance view to the embryo-geny of human
head, it starts as a primordium in the cephalic region of the embryo
which then in utero developed to the characteristic human head. As a
structure the head consist of the skull and the skull associated
sub-structures which assigned to perform number of biologic functions
like balance, cognition, hear, vision, smell and immune functions [3] (Table 1-3).
Immunology
The lymphatic system of human head constitute a vast
network of an interconnected lymph vessels and their associated lymph
nodes as well as countless lymph vessels. All these structures work
together to; drain, filter and cleanse the interstitial fluids and
destroy the harmful pathogens that may infect human head. The immune
system of human head is formed from three main components .The common
mucosal immune compartment, the mononuclear phagocyte cell system and
the transcudate humoral as well as the migratory lympho-myeloid
phagocytes from lymphoid origins. These compartments include natural,
cross-road and adaptive immune events outcomes [4,5].
Mucosal Immune System
Mucosal immunology is one of the discipline of
medical immunology. It concerned with the study of the mucosal immune
system (MIS). MIS is composed of lymphoid tissues that are associated
with mucosal surfaces of the; gastrointestinal, respiratory, and
genitourinary tracts as well as skin [Though some debate]. Such a system
has a number of features that differentiate it from the systemic
lymphoid system. These are including; Mucosal immunoglobulin [IgA, IgM
and to lesser extent IgG with tissue microenvironment dependent
dominance], mucosa specific regulatory or effector T cells and
mucosa-oriented cell homing system in several compartments .The primary
function of MIS is to provide defense at mucosal surfaces. It can be
divided into organized lymphoid tissue [M cells, Dome area cells,
follicular T cells and follicular B cells] covering the
gastrointestinal, respiratory and genitourinary tracts. And diffuse
lymphoid tissue in lamina propria, epithelia, and stroma of exocrine
glands compartments. The organized one is that acting as inductive sites
and the diffuse one devoted to the interaction with immune cells [6].
Mucosal Immune Mecanisms in Human Head
Intranasal specific immune priming provides a
productive means for inducing mucosal immunity at the head regions and
distal mucosal tissues via common mucosal immune system. This induction
of effector local cells in the nasal cavity is possible due to the
proximity of the draining lymph nodes where initial encounter between
antigen and lymphocyte occur. These tissues which support the induction
of immunity for oral cavity associated salivary glands are collectively
known as Cranium- oral and nasal lymphoid associated tissues [CONAL].
The CONLAT encompasses the facial or parotid glands located posterior to
the parotid gland, the submaxillary glands, the superficial cervical
lymph nodes located anterior to the submaxillary glands located dorsal
to the brachial plexus deep in the musculature of the neck. During the
intranasal immunization, submaxillary lymph drain the nasal submucosa,
cervical lymph nodes drain the nasal associate lymphoid tissue.
Submaxillary lymph nodes, the brain and the parotid gland tissue are
important in draining the skin of the head and neck as well as
conjunctiva. High percentage of L select in+ lymphocyte in CONALT
provide evidence that peripheral address in and homing receptors are
important in lymphocyte trafficking to and from nasal passages and the
salivary glands and the pathing of lymphocyte homing to the CONALT
differ greatly from those of the gut. This means that not all mucosal
tissues are phenotypically or functionally behave as intestinal tissue
and variability among the lymphoid tissues of PLN, SMLN, CLN to effect
distal mucosal immunity [7-9].
Conjunctiva associated lymphoid tissue in human eyes
occur in different forms. First as diffuse lymphoid tissue of lymphocyte
and IgA producing plasma cells formed a thin layer of lamina propria.
The overlaying epithelium produce secretory component. Conjunctival sac s
showed organized lenticular shaped follicles containing B cells and
lympho-reticular cells embedded in LP. Conjunctival crypts do contained
organized and diffuse lymphoid tissues. Lacrimal drainage system
lymphoid tissues contained lymphoid tissue of same nature. High
endothelial veinules present in all conjunctiva and lachrymal drainage
system. SIgA is locally produced in human conjunctiva [10-12].
Ear associated lymphoid tissue was found Eustachian
tube ,middle ear and mastoid process .Its presence was proved in those
with otitis media. MALT showed wedge shaped distribution through middle
ear and Eustachian tube. Bony parts of ET have shown MALT both in
tympanic and pharyngeal portions .The presence of MALT in the ear is
being age dependent and infants were found devoted from it. Ear
infection mediate development of MALT [13,14].
Nose associated lymphoid tissue NALT is taken as
constitutive structure of nose local immune system and as a target
tissue in strategies of local defense and as inductive site for
vaccination .It is morphologically distinct from that of Waldeyers ring.
Human NALT was found disseminated in the nasal mucosa with typical
morphological features mainly in concha [15,16].
Mucosal Immune Compartments of Human Head
Brain [7-9]
Contour structure: The brain is encased within
the bones of the skull. The brain consists of three main regions as
cerebrum, cerebellum and the stem .The brain stem serves as the relay
between the brain and the spinal cord.
Immune compartments: Cranium associated lymphoid tissue, glial cell system, and systemic migratory phagocyte cells.
Immune functions: Mucosal antibodies local
defense functions against infections .Glial cell system produce local
cytokines with phagocytic functions and served for brain tissue building
as well as signaling molecules in local immune reactions.
Eye [10-12]
Contour structure: The eyeball is made up from
three concentric coverings which encase the various transparent media
and the photosensitive retina. This coat consists of two regions,
transparent outer cornea and white the sclera. Sclera behind the cornea
is opaque and mainly of protective function.
Immune compartments: Conjunctiva associated
lymphoid tissue, lachrymal gland draining associated lymphoid tissue.
Natural immune barriers like eye brow, eye lids and lachrymal apparatus.
Immune functions: Local mucosal immune responses, SIgA and the natural immune barriers.
Ear [13,14]
Contour structure: Human ear consists of
external, medial and internal regions. The external ear includes the
pinna and the external audatorymetus, the tube from the outer ear to the
ear drum. The middle ear is the cavity between ear drum and the bony
wall of the inner ear, it contains three small bones the incus, mallius
and the stapes.
Immune compartments: Eustachian tube associated lymphoid tissue, ear wax, ear pinna.
Immune functions: Mucosal immune responses, natural immune barriers of infection and SIgA for local defense of ear infections.
Nose [15,16]
Contour structure: The gross topographic anatomy of human nose appeared as a protruding part of the face that bears nostrils.
Immune Compartments: Nasal associate lymphoid
tissue as a part of the cranial-oral and nasal associated lymphoid
compartment. As well as the nasopharynx associated lymphoid tissue.
Immune functions: Local nose immune responses. Mucosal inductive site. SIgA prevents local nasal infections.
Oral cavity [17,18]
Contour structure: The mouth, it is located at
the beginning of the gastrointestinal tract. It is enclosed on the
sides by the lips and checks, above by the hard palate and the soft
palate and below by the floor of the mouth and the tongue .the floor of
the mouth lies in a horseshoe around the tongue and is continuous with
the gingiva and tongue.
Immune compartments: Oral associated lymphoid
tissue as a part of the Cranial-Oral and nasal Associate lymphoid
tissue. Migratory lympho-myeloid phagocyte cells.
Immune functions: Oral mucosal immune responses, oral immune tolerance and oral inductive site. SIgA for local oral defense of infection.
Waldeyers Ring [19-21]
Contour structure: It is mucosal associated
lymphoid tissue MALT that consists of, lingual tonsils, palatine
tonsils, tubal tonsils, nasopharyngeal tonsils and small collection of
lymphoid tissues. These five tonsils surrounded the nasal and oral
cavities of the head. Two lingual, two palatine and one pharyngeal. Each
tonsil is a dense mass of lymphoid tissue covered in mucosal membrane
continuous with the surrounding tissues.
Immune compartments: Tonsillar lymphoid tissue as a part Waldeyers ring associated lymphoid tissue.
Immune functions: Local trapper of the invading pathogens, mucosal inductive site, and local mucosal responses.
Skin [22]
Contour structure: Skin is composed of three
layers. The epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. The dermis
contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles and sweat glands .The
deeper subcutaneous tissue is made up of fat and connective tissue.
Immune compartments: Skin associated lymphoid
tissue. It composed of; Langerhans cell system, keratinocytes, lympho-
reticular cells, skin seeking lymphocytes and the skin draining lymph
glands [As a term to mucosal compartment is still a subject of debate].
Immune functions: Local skin immunity against infections. Natural immune barrier
To know more about Open Access Journal of
Head Neck & Spine Surgery please click on:
To know more about Open access Journals
Publishers please click on : Juniper Publishers

Comments
Post a Comment